Is Your Soy Sauce And Vinegar Bottled In Glass Or Plastic?
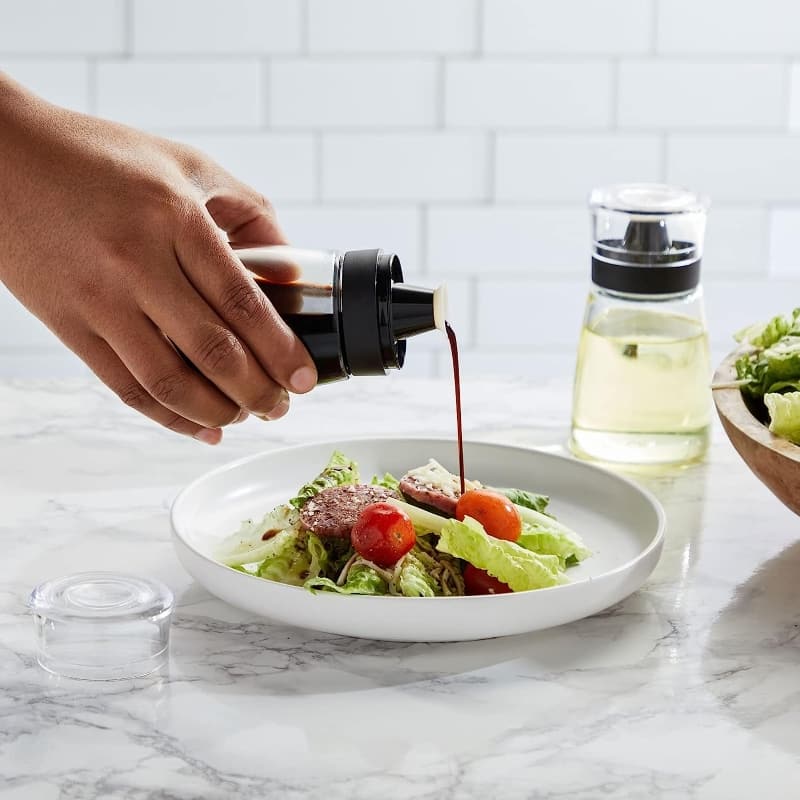

When it comes to flavor enhancers like these, the container matters. Glass and plastic are two common options, but how do you choose? Plastic seems cost-effective and durable, but let's explore the clear advantages of glass bottles for storing your culinary essentials.
Why the obvious edge for glass bottles when it comes to soy sauce and vinegar?
Glass containers undergo thorough testing, and their stability surpasses that of plastic. Cooking involves high temperatures, and glass's stability prevails under such conditions, preventing the release of harmful substances that can occur in plastic bottles.
While plastic containers for sauces and vinegar are subject to migration tests to ensure safety, their stability under high heat is still uncertain. Studies reveal that plastic bottles can release hazardous substances at elevated temperatures, posing health risks that may go unnoticed. Glass containers, especially for soy sauce and vinegar, remain the preferred choice in the market.
Using plastic beverage bottles for sauce and vinegar – a risky practice!
Some folks use plastic bottles for soy sauce and vinegar, even transferring them to smaller containers for convenience. Elderly individuals might resort to repurposing plastic beverage bottles. However, reusing plastic bottles for edible liquids raises concerns about safety.
Research indicates that repeated use of plastic bottles can lead to the formation of carcinogenic substances over time, posing significant health risks. Packaging tests on PET plastic bottles demonstrate that migration rates of phthalates (a type of plasticizer) are nearly 20 times higher in acidic liquids like soy sauce and vinegar compared to water.
Furthermore, vinegar's low pH and the use of antimony-based catalysts in plastic bottle production create conditions where migration rates increase. Hence, using plastic bottles to store soy sauce and vinegar escalates migration of harmful substances, a concern largely mitigated by glass containers.
How harmful are the substances migrating from plastic bottles to human health?
Plastic products contain leachables, including plasticizers. These toxic substances are carcinogenic, mutagenic, and teratogenic. Prolonged consumption of food contaminated by plasticizer residues has been linked to symptoms such as dizziness, headaches, nausea, loss of appetite, memory decline, and anemia.
Another group of substances, like antimony used in plastic production, can detrimentally impact normal metabolism. Although small doses may not exhibit pronounced effects, long-term accumulation can lead to irreversible damage across various organs and systems.
Hence, when choosing staples like soy sauce and vinegar, opt for glass or ceramic containers over plastic. Compared to plastics, these materials exhibit fewer instances of contaminant migration. So, whether it's original packaging or repurposed containers, prioritize glass and ceramic for your culinary essentials.
Next page: 4 Reasons Explain the Difference Between Bottled and Canned Beer